The minimum wage is a statutory wage floor that defines the minimum amount per hour worked and is regulated by the Minimum Wage Act (MiLoG). Fines can be imposed for non-compliance. The minimum wage is currently 12 euros per hour, an increase of 1.55 euros per hour worked compared to the previous level (10.45 euros). The new regulation has been in force since 1.10.22.
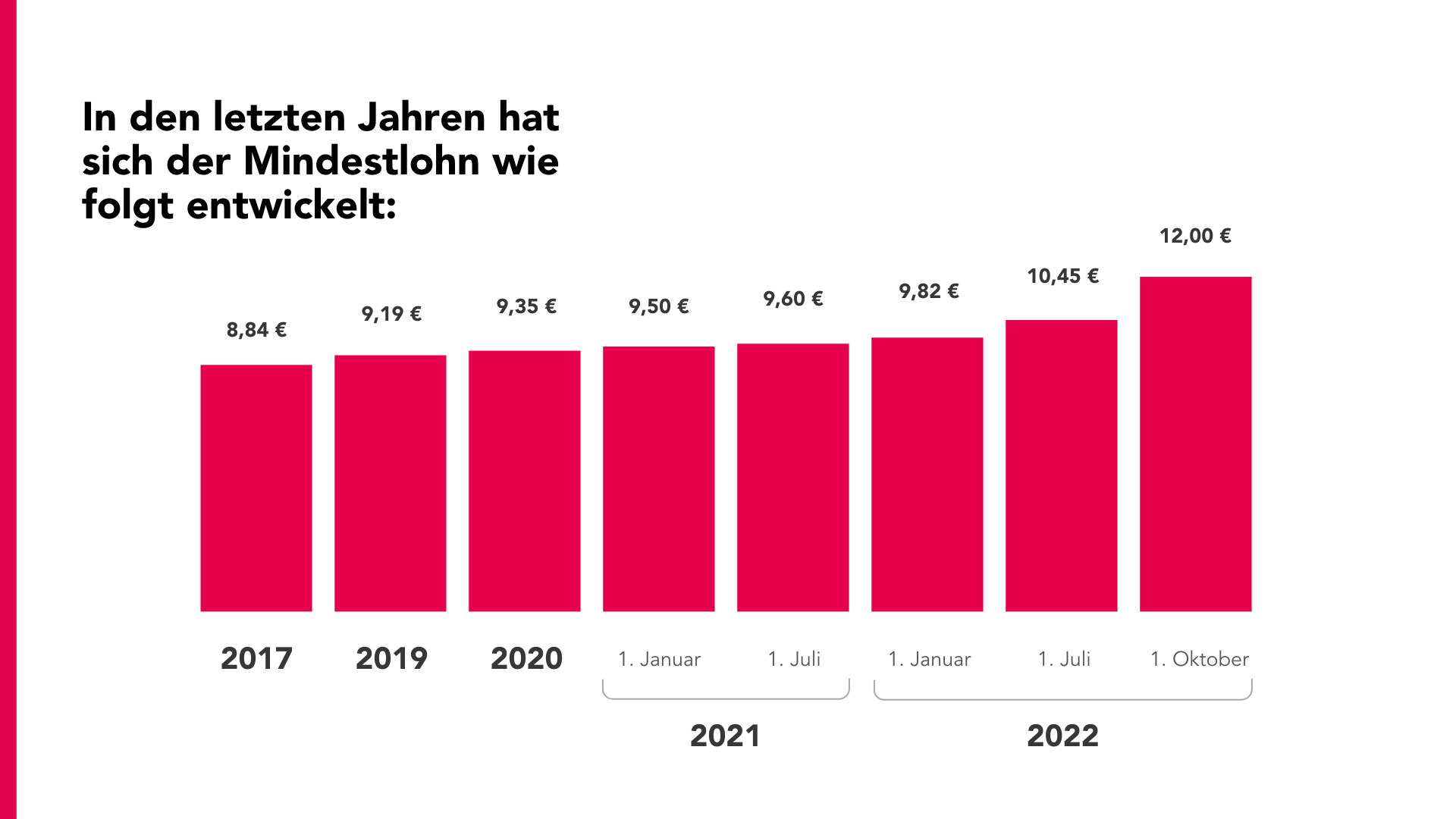
- 2017: 8,84 €
- 2019: 9,19 €
- 2020: 9,35 €
- 2021: 9,50 € (January 1), 9,60 € ( July 1)
- 2022: 9,82 € (January 1), 10,45 € (July 1), 12,00 € (October 1)
In 2015, the Germany-wide minimum wage was initially set at 8.50 euros. Prior to this introduction, there were already set wage guidelines, but these only applied to certain industries and were based on negotiations between employers and trade unions. Interestingly, at the beginning of 2022, Germany ranked sixth in an EU-wide comparison of statutory minimum wages (as of Jan. 1, 2022) in a survey by the German Institute of Economic and Social Research (WSI). At that time, only Luxembourg, the Netherlands, France, Italy and Belgium had set a higher minimum wage.
Therefore, the minimum wage must be continuously adjusted
The minimum wage prevents price dumping and thus ensures fair competition between companies. By setting a lower limit for wage payments, companies are prevented from keeping their prices unrealistically low by exploiting workers. This creates fair conditions that benefit both employers and employees.
The minimum wage helps to prevent underpayment and maintain social balance. By providing workers with an adequate income, it improves their financial stability. This in turn has a positive impact on society, as fewer people are at risk of poverty and a higher level of social participation is made possible.
By ensuring an adequate income for employees during their working lives, a solid financial basis is created that enables them to lead a dignified life in old age. In addition, the minimum wage enables all employees to participate in society and to build up financial reserves.
Innovations to the minimum wage are the responsibility of an independent commission
Every two years, the independent Minimum Wage Commission, consisting of representatives of collective bargaining partners, makes recommendations to the German government on adjusting the minimum wage. In doing so, the commission takes into account various factors such as appropriate minimum protection for employees, fair competitive conditions and job security. The commission's decisions are based on the development of collectively agreed wages in Germany.
The Minimum Wage Commission continuously monitors the effects of the minimum wage and provides the federal government with a comprehensive report every two years.
In accordance with the coalition agreement, the federal government increased the statutory minimum wage to twelve euros per hour in a one-time adjustment and this measure was implemented. Future adjustments to the minimum wage will continue to be made based on the recommendations of the Minimum Wage Commission. The next adjustment will be made for the first time on June 30, 2023, with effect from January 1, 2024.